How GraphQL is taking over backend development: A deep dive into Spring Boot.
Deep Dive into GraphQL and its presence into backend development
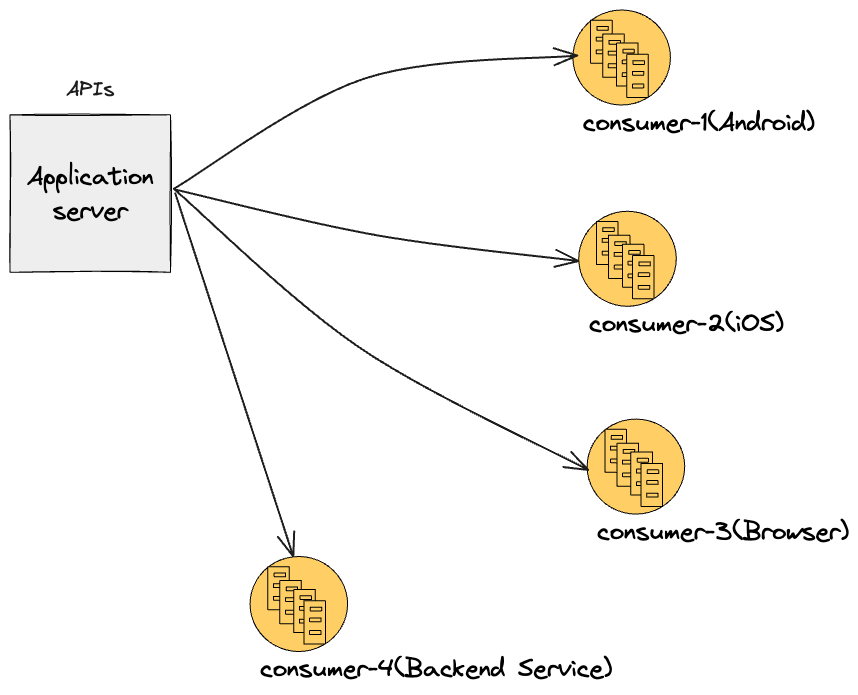
If you are a backend developer, have you ever given a thought on your backend application can do more than REST in terms of implementing APIs.
There are several options available
gRPC for http 2.0
GraphQL over HTTP
But point is why do we still using REST ? when we already have few other options available better than REST.
Is REST better today ? for exposing public APIs ?
Answer, is we would not say better, but it is a better fit if someone has high preference on
Easy Implementation and Understanding of architecture style.
Stateless
Wide Adoption and Community support
API versioning
Lower development and maintenance costs
So if you count there are already several benefits of using REST today but remember the fact that it comes with few problems as well.
What are the pain areas of REST ?
Let’s consider below JSON Response for one of the REST API.
{
"order": {
"pos": "retail-app",
"orderCreatedAt": "2023-05-22 12:04:44",
"invoice": {
"invoice_number": "number123",
"customer_name": "suchait",
"purchasedItems": [
{
"product_id": "id12",
"product_name": "pname12",
"quantity": 2,
"price": 120.5
}
],
"total_amount": 320.5
}
}
}Over Fetching
API can return more data than unnecessary in a response. for example
There will be enough chances that consumer-2 doesn’t want all information that is present in json response.
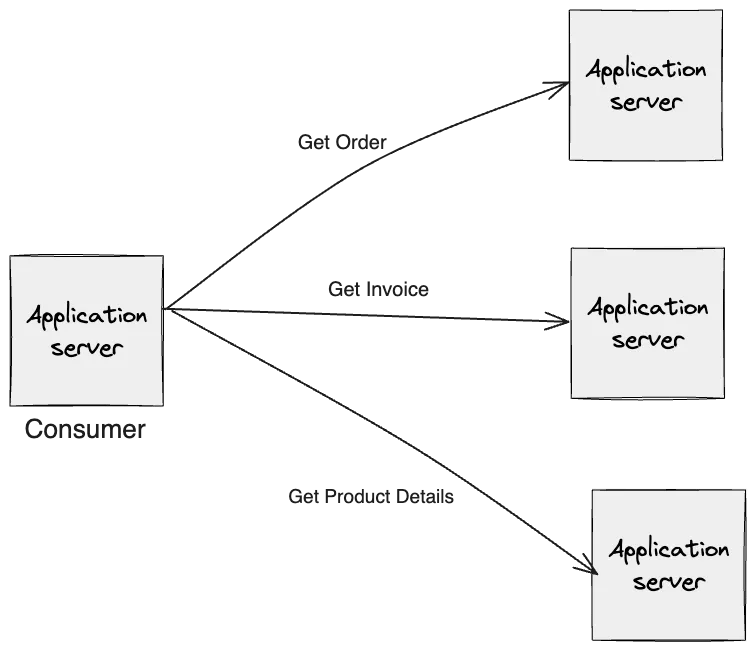
Under Fetching
API might not return the enough data, requiring multiple requests to different endpoints to gather all necessary information.
Rigid Structure
Fixed nature of REST endpoints can make it difficult to adapt to changing requirements.
Limited Query Capabilities
REST APIs typically lack the sophisticated query capabilities found in systems like GraphQL. Filtering, sorting, and pagination often need to be implemented manually and can vary between APIs.
No Standard API Specification
We can have an API specifications but only when development team decides to implement swagger.
Yes, we understood there are couple of challenges with REST, can we use graphQL to overcome these ?
Answer is yes, we can in fact that is the reason graphQL exists today - graphQL offers solutions to all problems listed above that comes as part of REST.
Fundamentals Concepts of GraphQL
Schema
central concept in GraphQL. It defines the structure of the data that can be queried and manipulated through the GraphQL API. It is written using the Schema Definition Language (SDL).
Types: Define the shape of the objects that can be queried or manipulated. Types can be scalar (e.g.,
Int,Float,String,Boolean,ID) or complex (object types, enum types, etc.).Fields: Define the properties of a type. Each field has a type, and fields can also have arguments.
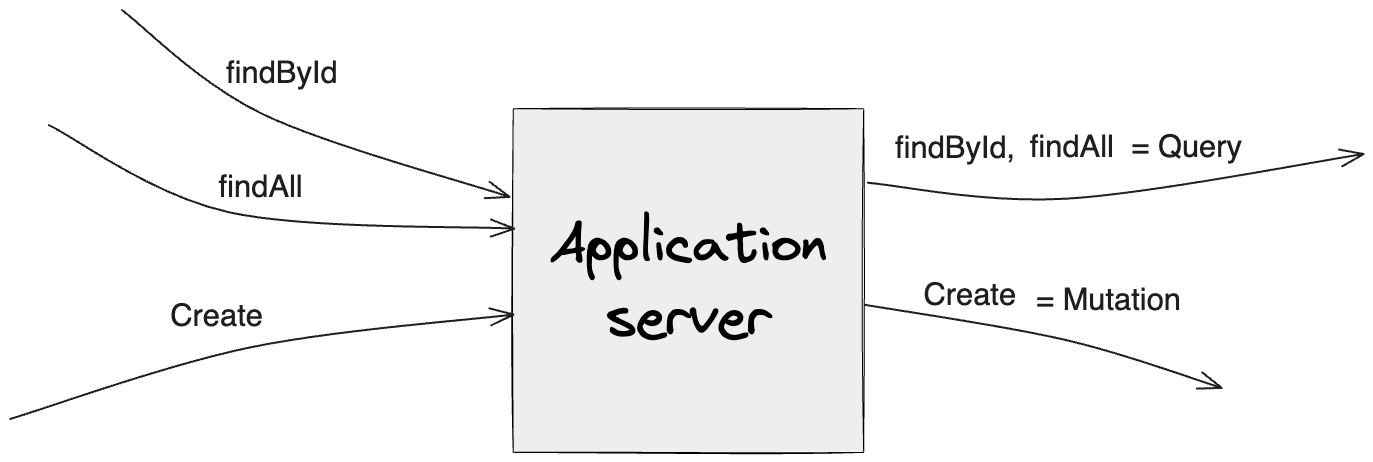
Query Type: Defines the entry points for read operations.
Mutation Type: Defines the entry points for write operations.
type User { id: ID! name: String! email: String! } type Query { users: [User!]! user(id: ID!): User } type Mutation { createUser(name: String!, email: String!): User! }Queries
Queries are used to fetch data from a GraphQL server. They allow clients to specify exactly what data they need, avoiding over-fetching and under-fetching.
{ users { id name email } }Mutations
Mutations are used to modify data on the server (create, update, delete). They can return the modified data, allowing the client to update its state accordingly.
mutation { createUser(name: "John Doe", email: "john@example.com") { id name email } }
Let’s understand few important concepts of graphQL by implementing it with Spring Boot.
Implementation with Spring Boot - Understanding graphQL fundamentals with development
Github Repo - https://github.com/suchait007/tutorials-graphql
You can download the above project in your local for better understanding.
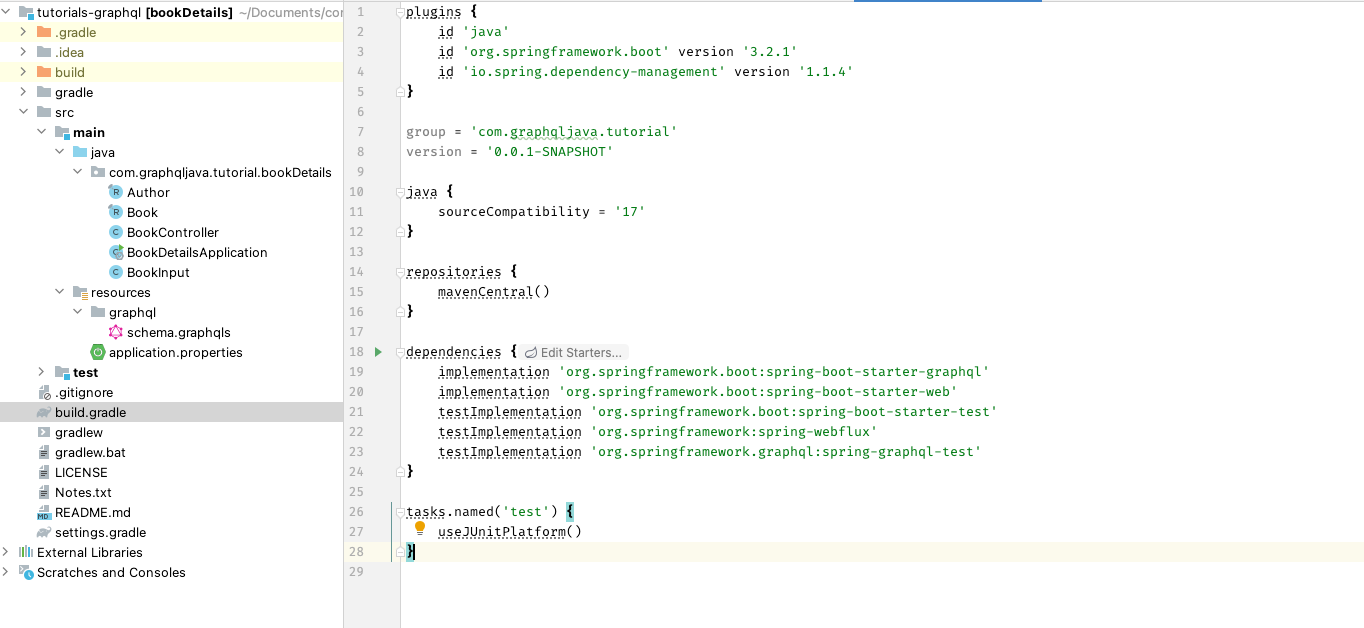
Add dependency org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-graphql to download graphQL related dependencies
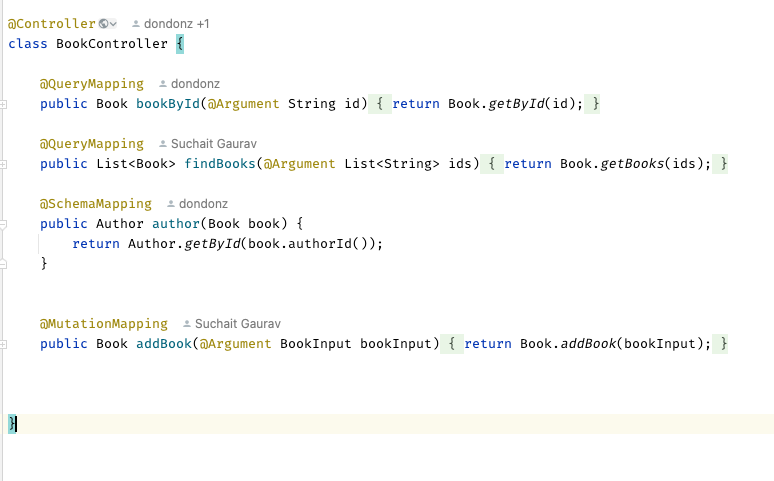
Now we need to create a Product Controller,
Once controller is ready now, let’s create a schema.graphqls file under /resources/graphql folder.
for service and other classes please refer github project.
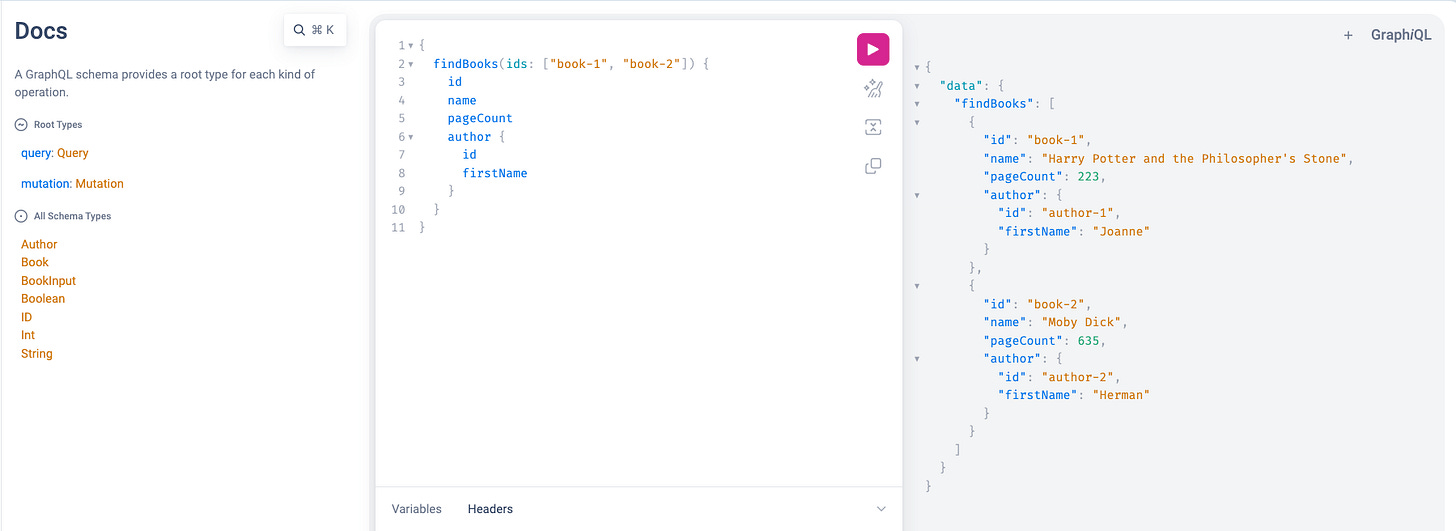
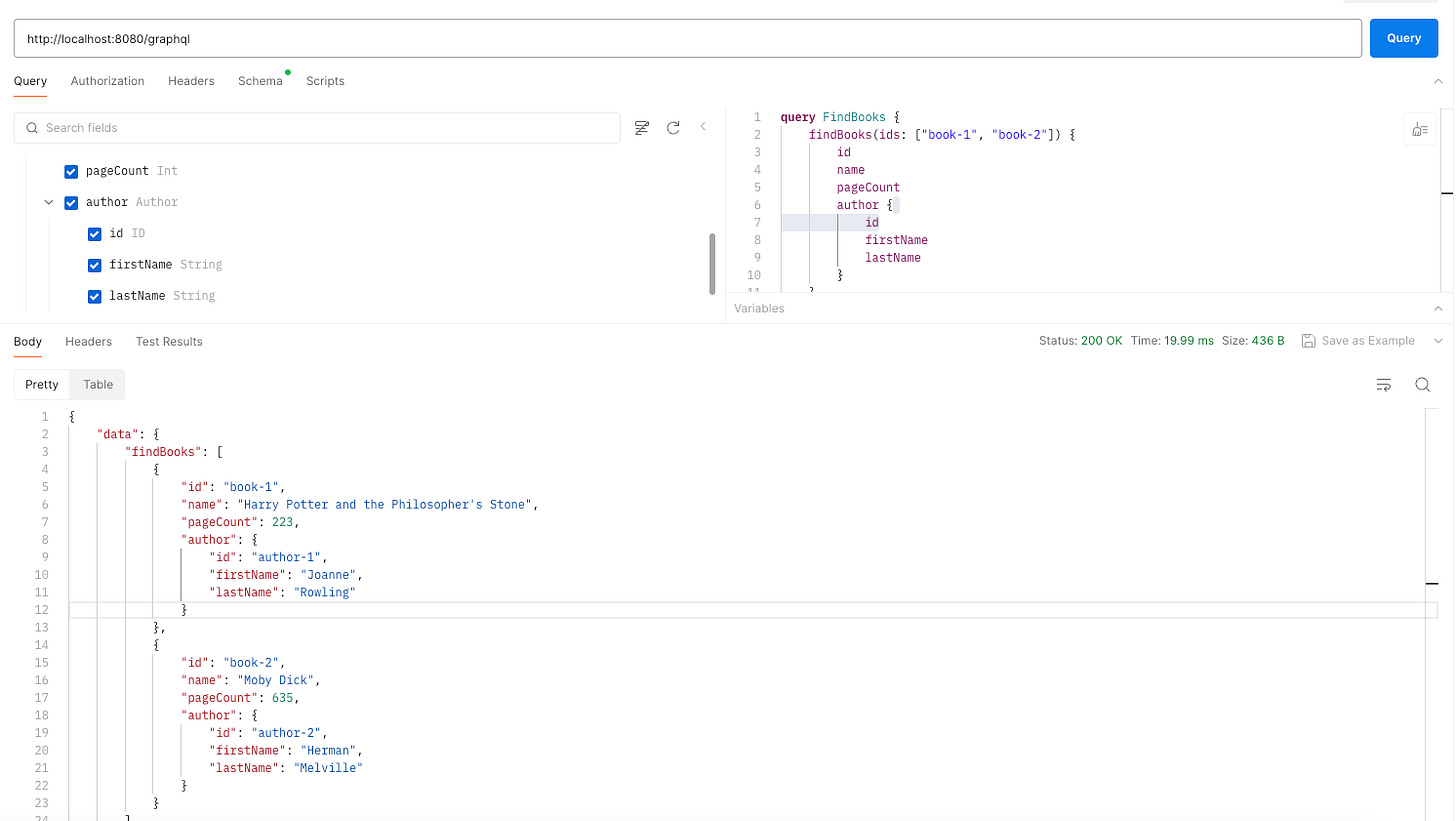
Now once we have defined all these important components we can open graphiql UI in order to get access to above mentioned query and mutation.
All queries and Mutations will be accessible at URL http://localhost:8080/graphql
graphiql - GraphiQL is an interactive in-browser tool for exploring GraphQL APIs, often referred to as an "IDE for GraphQL."
We can use Postman as well.
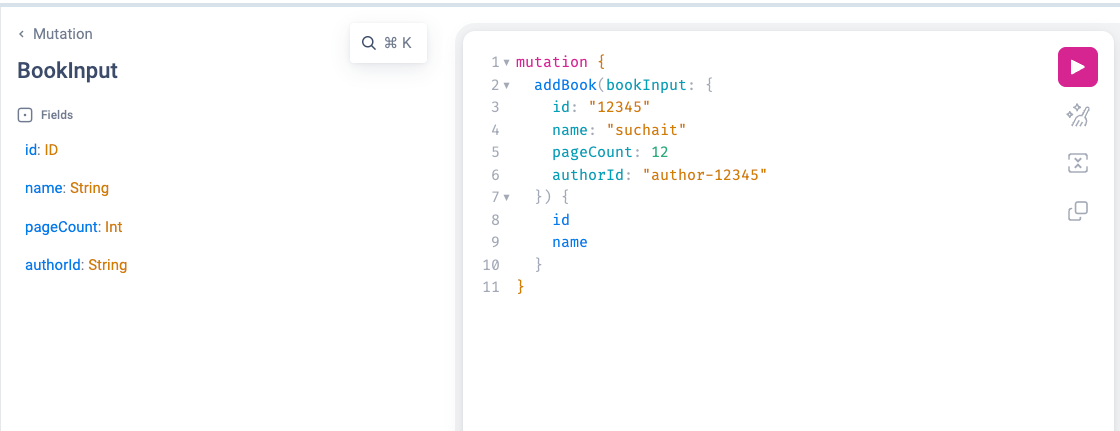
Running a Mutation
Now, by this time, we have enough information on what are the challenges with REST, how graphQL fixes it and most importantly using spring boot how can we implement graphQL.
Let’s have a final look if there are any challenges with graphQL.
Challenges with GraphQL
Learning GraphQL Syntax and Concepts
Developers need to learn new concepts like schemas, resolvers, and queries.
Understanding how to write efficient queries and mutations can be challenging.
Query Complexity
GraphQL queries can become complex and deeply nested, potentially leading to performance issues if not managed properly.
Optimising queries and ensuring they do not adversely affect server performance can be challenging.
Complexity in Securing Endpoints
Securing GraphQL endpoints requires careful consideration of query validation, authorization, and rate limiting.
Caching Challenges
Unlike REST, where caching mechanisms are straightforward due to the fixed nature of endpoints, caching GraphQL responses can be more complex.
Debugging Issues
Errors in GraphQL resolvers can be harder to trace and debug compared to traditional REST endpoints.
I hope this article helped you in understanding of REST vs GraphQL with deep dive into GraphQL.
If you really like my content you can subscribe me below.
Youtube Channel - https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpF3Y8AxzgYZnI8Zcf_G_fg
You can follow me on linkedin here - https://www.linkedin.com/in/suchait-gaurav-944479109/
Github Repo - https://github.com/suchait007
Thank you!