Database Sharding Explained: Discuss the concept of database sharding.
Deep Dive into Concepts of Sharding
Before starting this article, think about the situation where you have a big bang database running with lots of records in it ?
World without Database Sharding ?
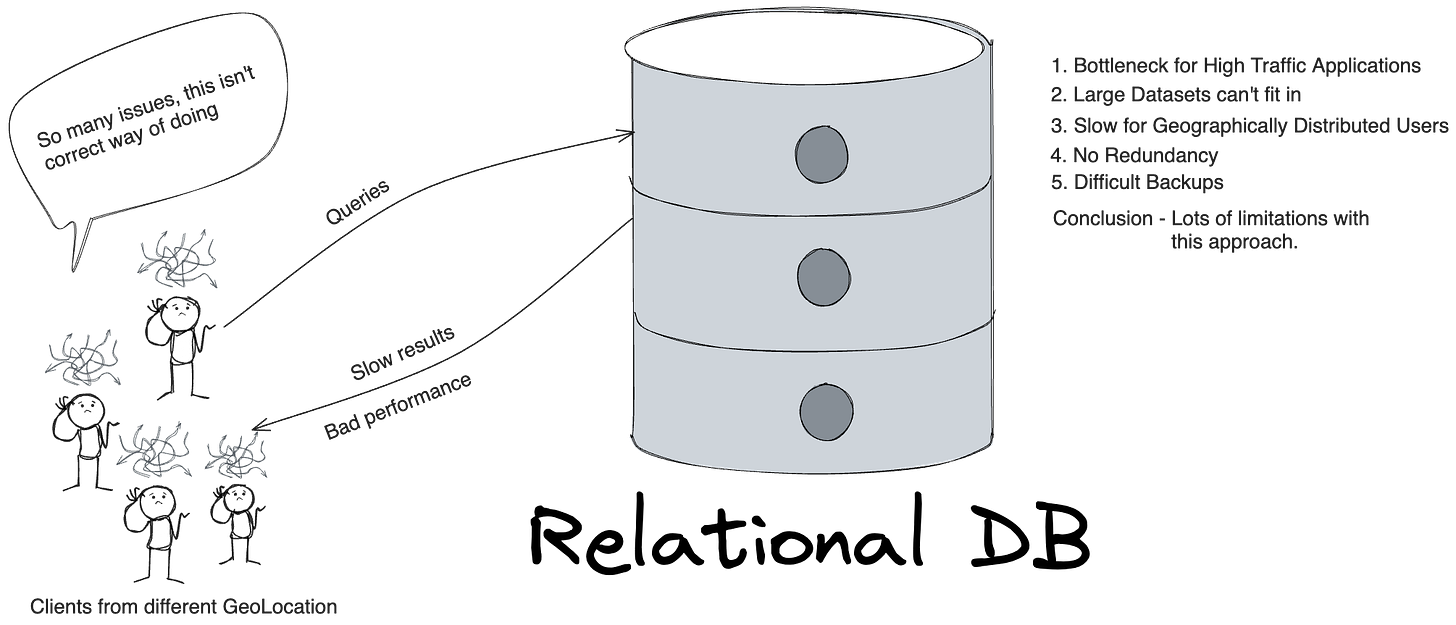
Think about a use case where a social networking site, with all data being handle in a big machine based database cluster/single database server.
By looking at the picture itself, you can think of how many issues there will be if we are using above kind of approach. Let’s discuss them all quickly.
Geographically Distributed Users
Users querying and performing operations around the globe will be slow as there will be lot of difference between server and the user.
Large Dataset
Single database approach will always a limitations in terms of space, no matter how much vertically you scale it in terms of infrastructure you will always end up having issues with infra resources.
High Traffic based Applications
Considering use case, where our application will be used world wide. There could be lots of users accessing it using features continuously which will be leading do frequent traffic on database and with this environment single database approach will always cause performance issues.
Difficult Backups and HA
With this above approach, it will be so difficult to manage backup and high availability for the server running, Assuming your single server has a lot of data not easy to handle.
Alright, by this time we understood there are so many issues following above database approach, now what could be possible solution of this ?
Database Sharding
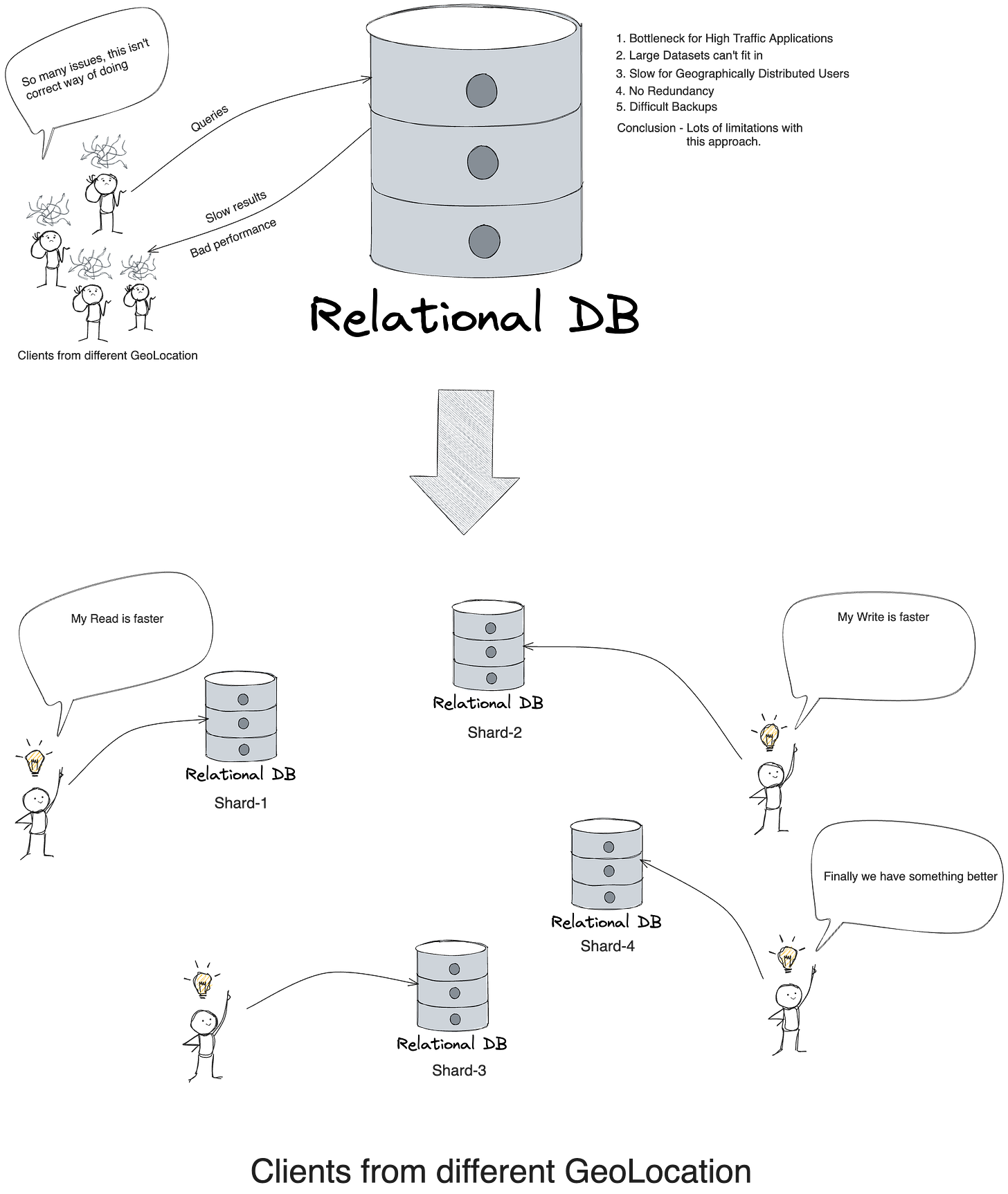
A possible solution of above problem is what if we break down the above database into different machines and distribute the data among it.
Every single machine that has small part of data is know as shard.
So database sharding is storing large database across multiple machines.
Till here we understood what is database sharding and what are the problem we had that it solved.
Now let’s understand using what all techniques we can implement database sharding.
Database Sharding Techniques
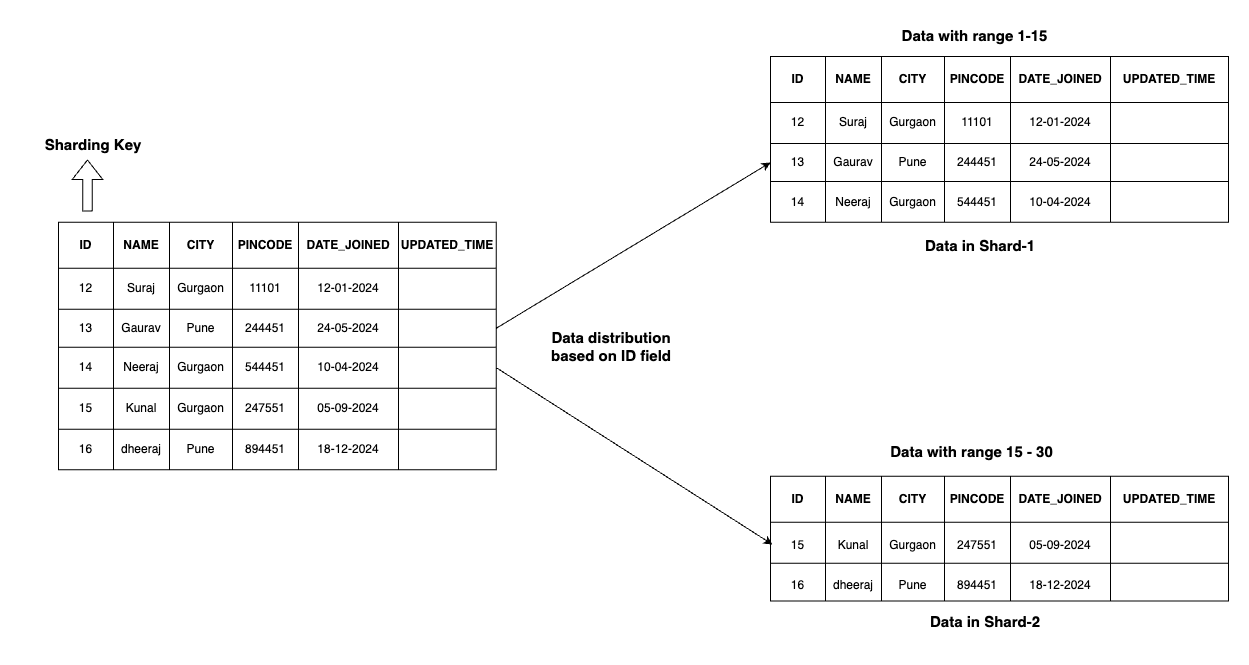
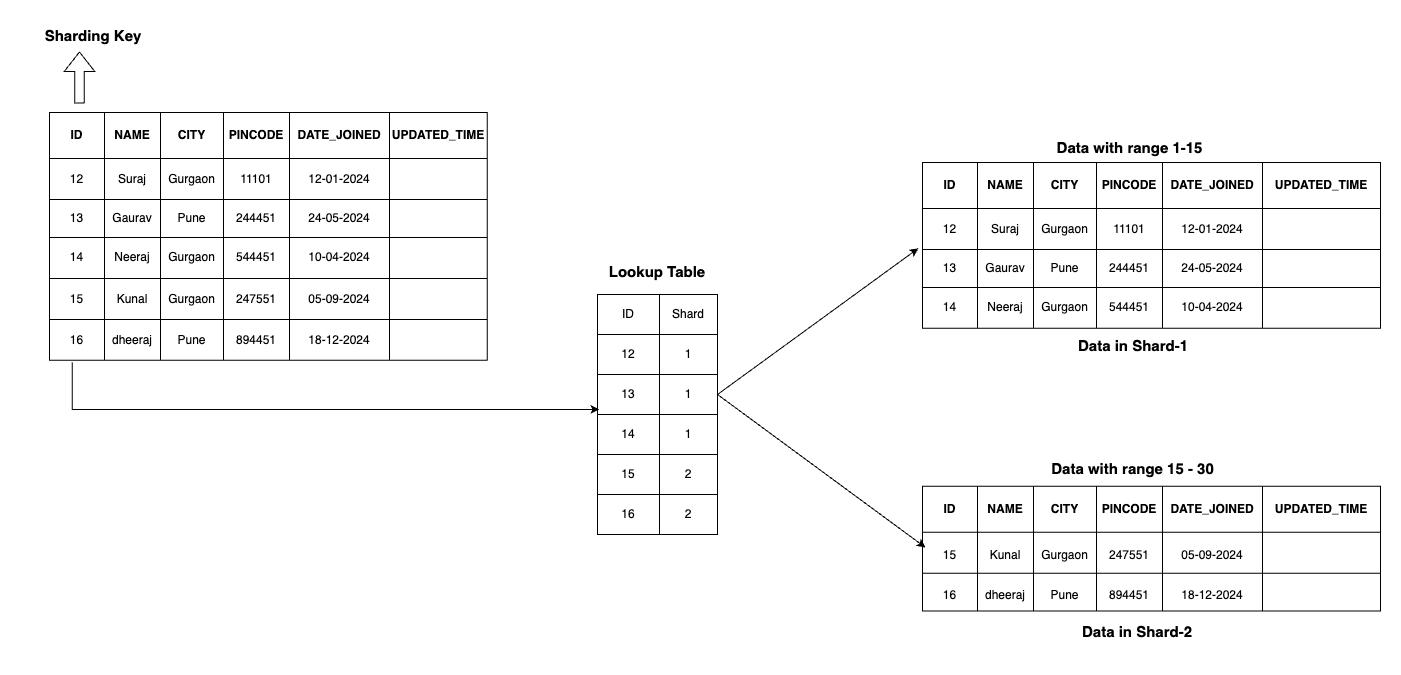
Range based Sharding
Data is divided into shards based on a specific range of values for a given partitioning key.
For example, in this case field “ID“ is the partition key (Sharding Key).
In range based sharding all queries which has ID from 01- 15 will routed to shard-1.
Accordingly all queries which has ID greater than 15 - 30 will be routed to shard-2.
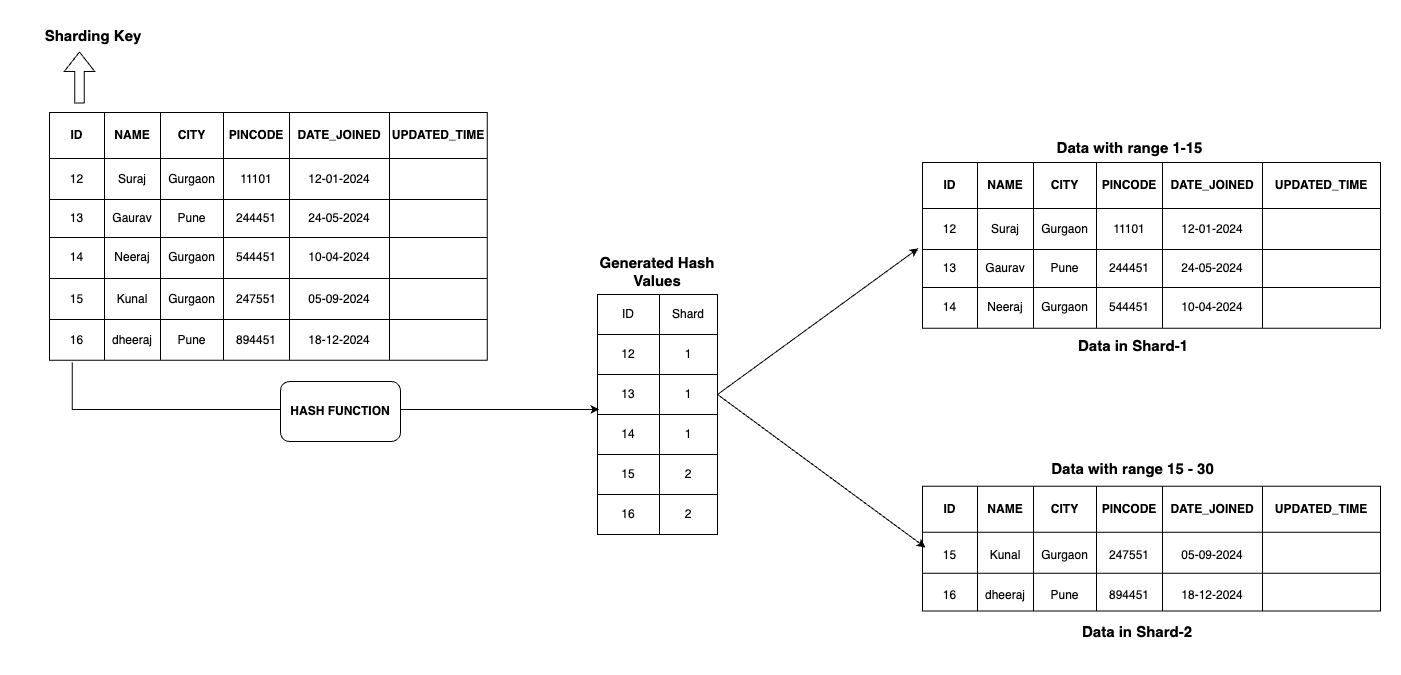
Hash based Sharding
This sharding approach, has a hash function which is applied on partition key and generates a hash value which indicates a shard that will has this data.
The good part of this sharding technique is - it leads to even distribution of partition keys.
Directory based sharding
This technique uses a lookup table to check for the shard detail for a parition key from lookup table.
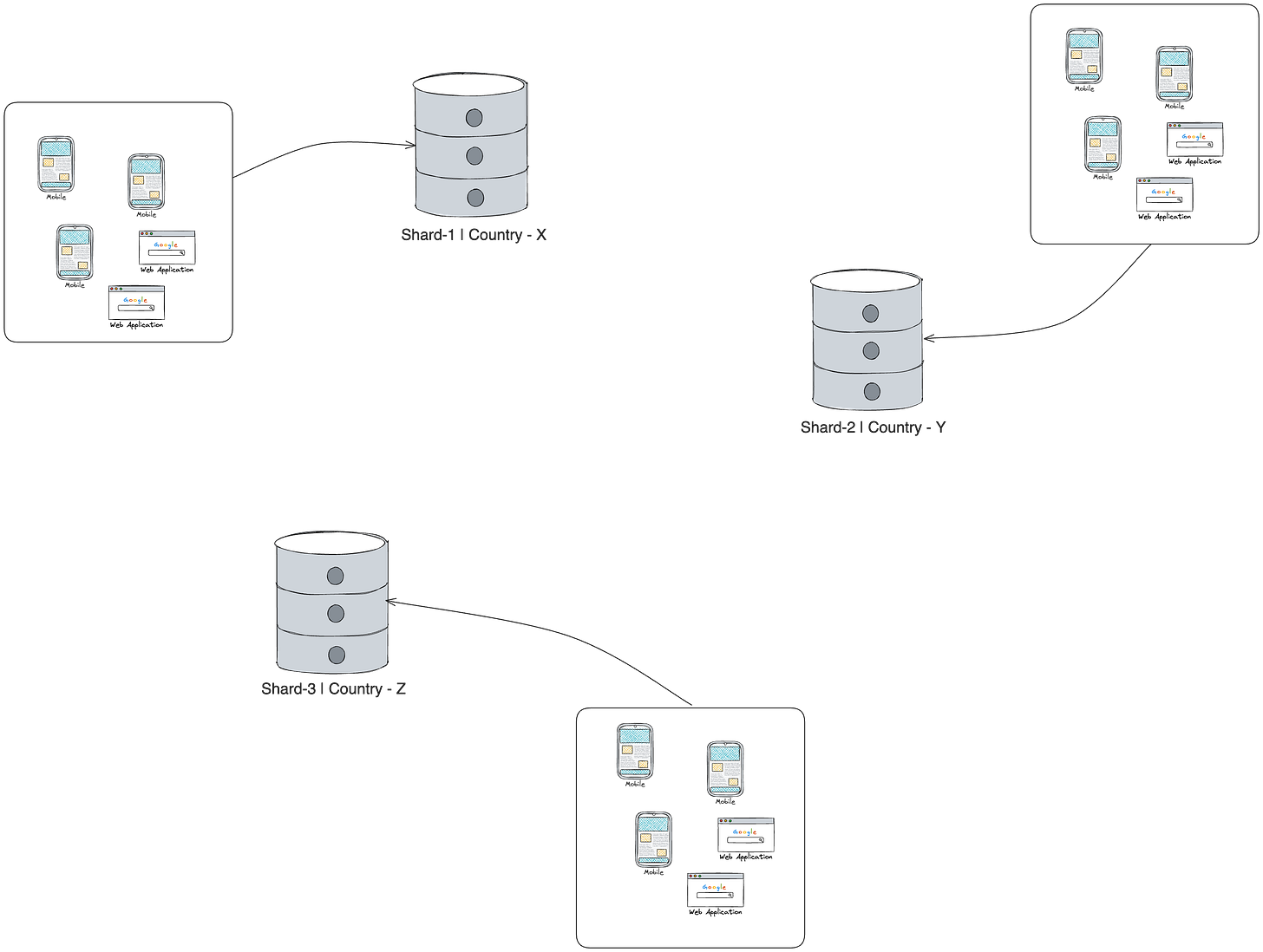
Geograhical Sharding
This approach, involves partitioning data based on geographical locations, such as countries or regions.
This approach helps in reducing latency and improve performance.
Problems with Database Sharding
Complexity in Implementation and Maintenance
Sharding adds significant complexity to the application and database architecture. Developers need to handle the logic for distributing data across shards, which can complicate query writing, data insertion, and retrieval processes.
Data Distribution Challenges
Achieving an even distribution of data across shards can be difficult.
Rebalancing Shards
As the data grows, some shards may become too large, necessitating the rebalancing of data across shards.
Cross-Shard Joins and Transactions
Performing joins and transactions across multiple shards is challenging and often results in reduced performance. Applications need to be designed to minimize or avoid cross-shard operations.
Schema Changes:
Implementing schema changes in a sharded environment can be more complicated compared to a single database instance. Changes need to be applied consistently across all shards.
Application-Level Shard Awareness
The application needs to be aware of the sharding scheme to correctly route queries to the appropriate shard.
By this point, we understood in depth of database sharding hope this helped you.
If you really like my content you can subscribe me below.
Youtube Channel - https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCpF3Y8AxzgYZnI8Zcf_G_fg
You can follow me on linkedin here - https://www.linkedin.com/in/suchait-gaurav-944479109/
Github Repo - https://github.com/suchait007